LOST WAX CASTING
Precision casting specialized
for 3D complex shape
for 3D complex shape
We are confident about the lost wax casting technique, but still keep moving forward to improve our skills
Lost wax casting process is a method of metal casting that has been known for a long time. We have been developing the basic technology established in the United States, and we have a top share in precision casting in the general industrial field in Japan.
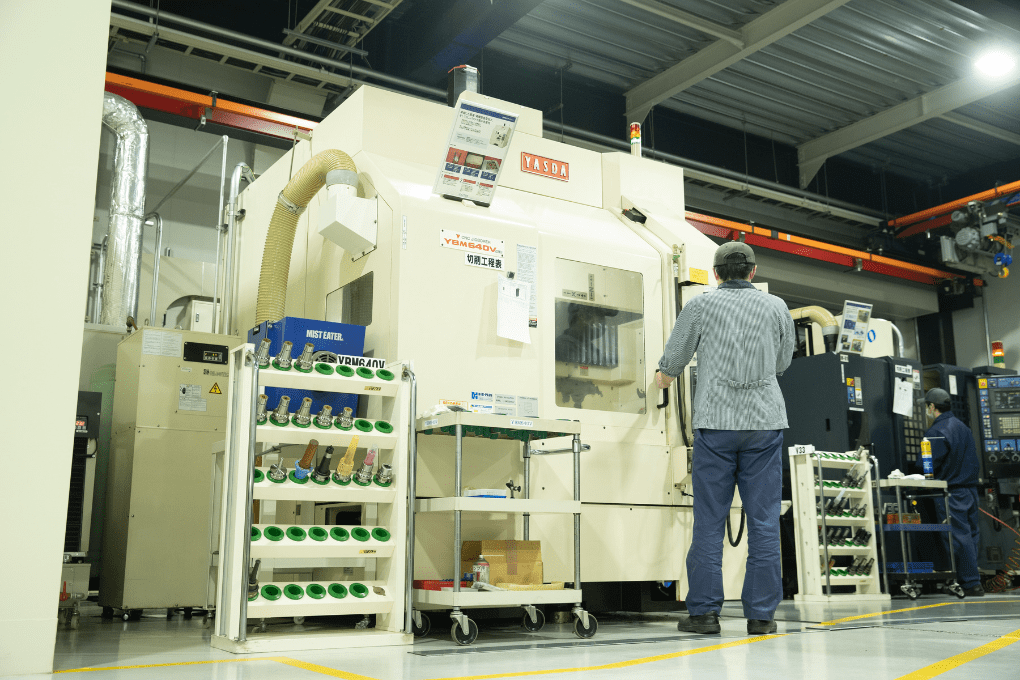
We can handle everything from mold making to the machining process at each base factory.
Also, we have a comprehensive system by cooperating with some partner companies that specialized in surface treatment, heat treatment, and assembly.
We can handle everything from mold making to the machining process at each base factory.
Also, we have a comprehensive system by cooperating with some partner companies that specialized in surface treatment, heat treatment, and assembly.
CASTEM Color

FEATURE
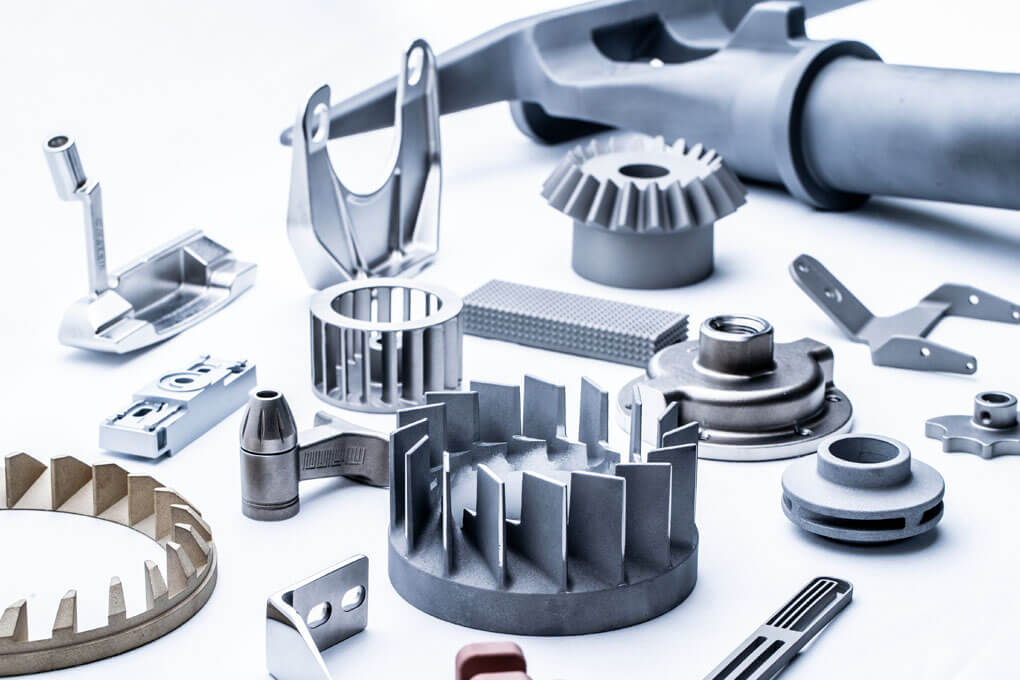
We have more than 30,000 experiences with lost wax casting, which is the largest number among lost wax manufacturers.
We are good at simple to complex 3D shapes such as hollow structures, undercut shapes, and gear profiles.
Also, we can handle various materials such as iron, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and some customer-specified materials.
We are good at simple to complex 3D shapes such as hollow structures, undercut shapes, and gear profiles.
Also, we can handle various materials such as iron, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and some customer-specified materials.
Examples of Proposals
01
Modification of Manufacturing Method
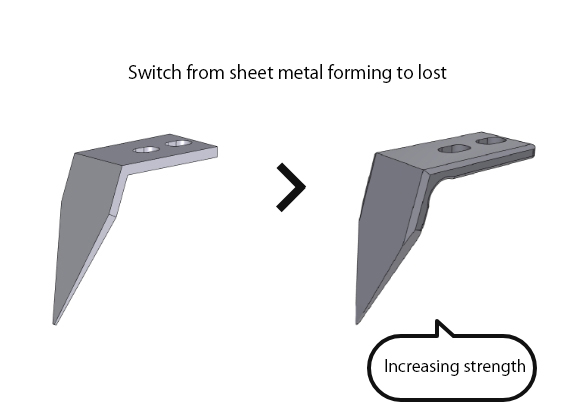
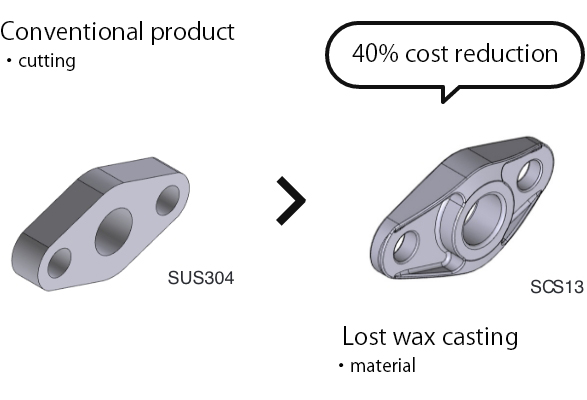
02
Integration
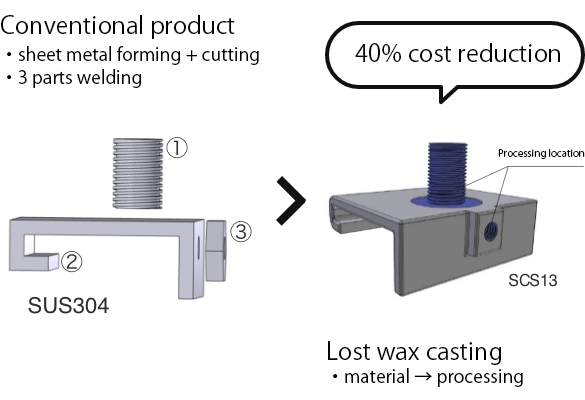
03
Reduction in Thickness and Weight
Manufacturing Process
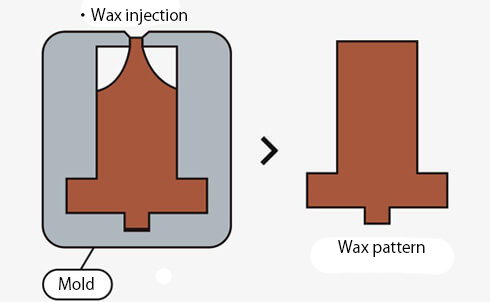
01. Wax molding
Create wax patterns by injecting wax into molds.
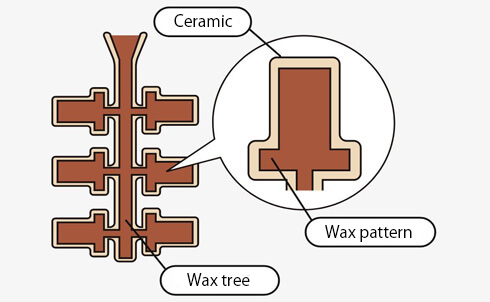
02. Ceramic coating
Coat about 4 to 6 layers of ceramic liquid and powder on the wax tree.
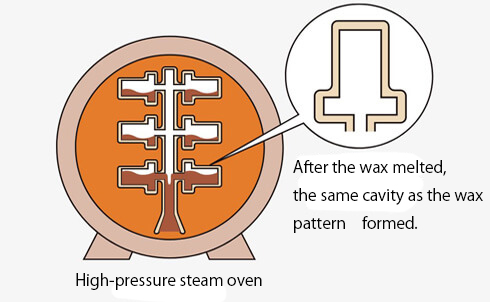
03. Dewaxing
Remove wax by high-temperature steam pressure.
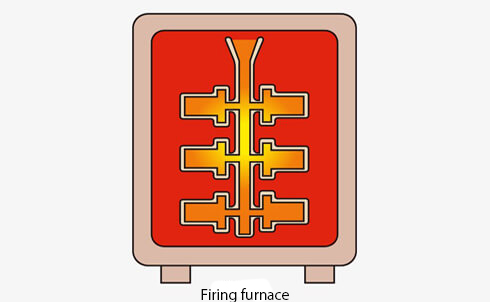
04. Mold firing
Burn out wax completely, and sinter ceramic mold.
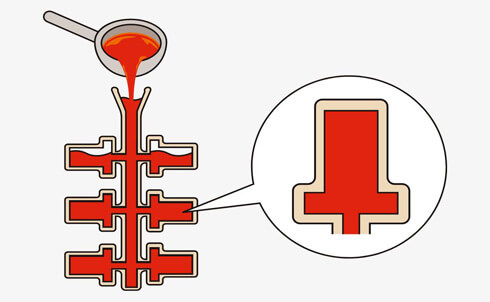
05. Casting
Pour molten metal into the mold.
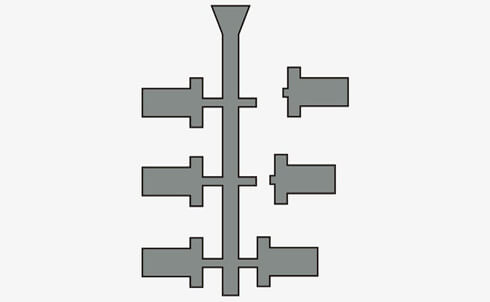
06. Cutting
Remove the mold and cut products from the tree.

07. Heat Treatment
Realize stable metal structures by heat treatment.
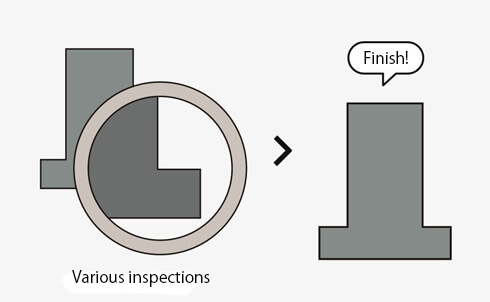
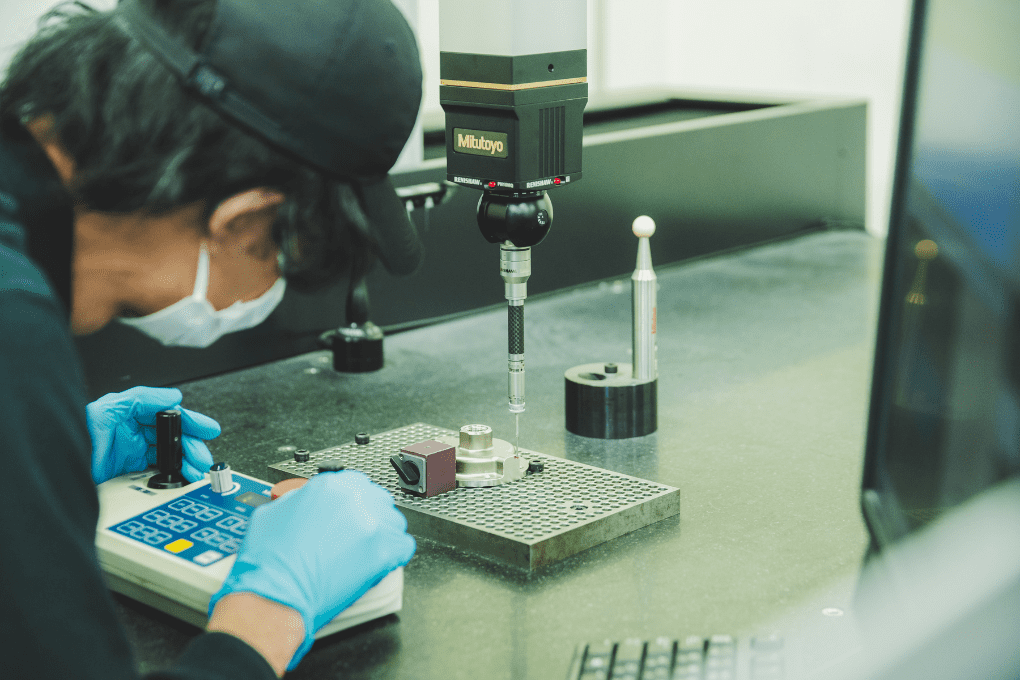
08. Inspection
Inspect the product based on various strict quality standards.
Catalog Download
Materials
| Classifications | Materials |
|---|---|
| Carbon steel | S25C, S45C |
| Chromium molybdenum steel | SCM415, SCM435, SCM440 |
| Nickel chromium steel | SNC415, SNC815 |
| Nickel chromium-molybdenum steel | SNCM220, SNCM439, SNCM616 |
| Tool steel | SK105, SKS3, SKD11, SK85, SKD61 |
| High-speed steel | SKH51, SKH57 |
| Austenitic stainless steel | SCS13 (SUS304), SCS14 (SUS316), SUS303, SCS19 (SUS304L), SCS16 (SUS316L), SCS18 (SUS310S), SUSXM15J1 |
| Martensitic stainless steel | SCS1 (SUS410), SCS2 (SUS420J1), SCS2A (SUS420J2), SUS440C |
| Precipitation hardening stainless steel | SCS24(SUS630) |
| Ferritic stainless steel | SUS430 |
| Duplex stainless steel | SCS11(SUS329J1) |
| Heat-resistant steel | SCH13, SCH21 ,SCH22 |
| Special steel | SUJ2 ,SUP10 ,SUM23 |
| Cast iron | FC200 ,FCD500 |
| Aluminum alloy | AC4C ,AC7A |
| Copper alloy | CAC102 (pure copper), CAC302 (HBsC2), CAC403 (BC3), CAC703 (ALBC3), CAC802 (SzBC2), CAC502A (PBC2), CAC203 (YBs C3), CrCu (chromium copper) |
| Cobalt alloy | Stellite 12 |
Tolerance Chart (mm)
| Dimension | Unspecified tolerance |
|---|---|
| 0 - 10 | ±0.15 |
| 10 - 25 | ±0.25 |
| 25 - 50 | ±0.40 |
| 50 - 75 | ±0.60 |
| 75 - 100 | ±1.00 |
| 100 - 125 | ±1.30 |
| 125 - | ±1.5% |
| Angular tolerance | ±1.5° |
Size Guides
| Minimum size | approximately 4cm |
|---|---|
| Maximum size | approximately 30cm |
| Minimum weight | approximately 30g (minimum thickness: 2mm) |
| Maximum weight | approximately 30kg |